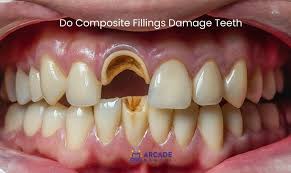
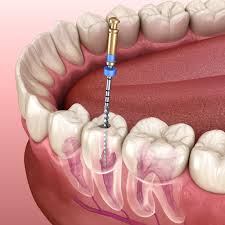
Cavities are holes, or areas of tooth decay, that form in your teeth surfaces. Causes include plaque buildup, eating lots of sugary snacks and poor oral hygiene. Treatments include dental fillings, root canal therapy and tooth extraction. The sooner you treat a cavity, the better your chance for a predictable outcome and optimal oral health.